Understanding the challenge
The application is really simple and it presents an option to decrypt a memory, based on user input. Annotated Ghidra decompiled code below:
void main(void)
{
ushort ppuVar1;
char inputNum [28];
int local_c;
do {
printf("Which memory would you like to review today (0 -> 3)? ");
fgets(inputNum,0x10,stdin);
ppuVar1 = __ctype_b_loc();
if (((*ppuVar1)[inputNum[0]] & 0x800) == 0) {
local_c = -1;
}
else {
local_c = atoi(inputNum);
}
decrypt_message(local_c);
} while( true );
}
No buffer overflow when reading the user input, or other obvious vulnerabilities. The highlighted condition checks whether the first character of user’s input is a digit or not, using the __ctype_b_loc function:
((*ppuVar1)[inputNum[0]] & 0x800) == 0
The decryption function is short as well, and easy to make sense of:
void decrypt_message(int param_1)
{
undefined8 local_28;
undefined8 local_20;
long local_18;
int local_c;
if (param_1 == 3) {
puts("-- ERROR -- [That memory has been locked away!] -- ERROR --");
}
else if ((param_1 < 4) && (-1 < param_1)) {
local_18 = *(long *)(messages + (long)param_1 * 8);
local_28 = 0xc3e2af1e8edad4c6;
local_20 = 0xee602548c0d4060c;
for (local_c = 0; *(char *)(local_18 + local_c) != '\0'; local_c = local_c + 1) {
putchar((int)(char)(*(byte *)((long)&local_28 + (long)(local_c % 0x10)) ^
*(byte *)(local_18 + local_c)));
}
puts("");
}
else {
puts("-- ERROR -- [That memory does not exist] -- ERROR --");
}
return;
}
Basically memories 0-2 are decrypted using a long XOR key, while any attempt to decrypt the 3rd one results in an error.
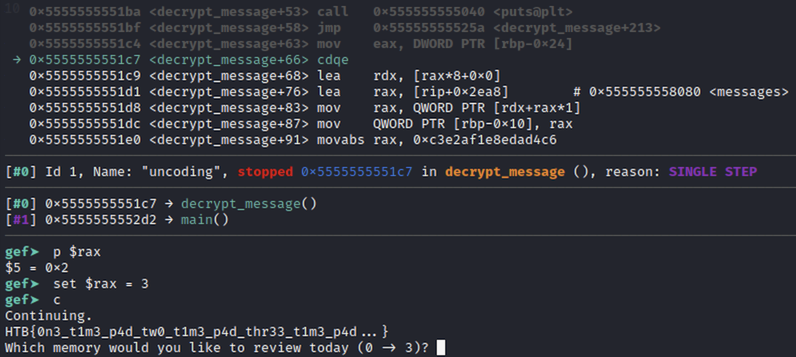
Solution
A quick way to recover the 3rd one is to run the binary under a debugger and patch the code on the fly in order to do the decryption for input parameter 3: